How to Read a Window Label
Posted
on April 1, 2020
Researching and shopping for replacement windows and doors can be a lengthy and confusing process for the average homeowner. On top of determining which style, material, brand and performance features you want it can be difficult to decipher the industry codes and ratings included on a window label. Window labels not only contain important industry information, but they also tell consumers more about the performance and energy efficiency of the product. Familiarizing yourself with these labels can make the overall experience more enjoyable and provide you with the knowledge you need to make an informed decision.
Energy Efficiency
First thing’s first, make sure you are selecting an energy-efficient brand. The ENERGY STAR® program is a government-backed program through the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that helps consumers make informed, energy-efficient decisions. The ENERGY STAR® logo is an indication that the product you’re looking at meets the energy requirements set forth by your state. This bright blue logo signifies that a product uses less energy, helps reduce your carbon footprint and can help save you money.
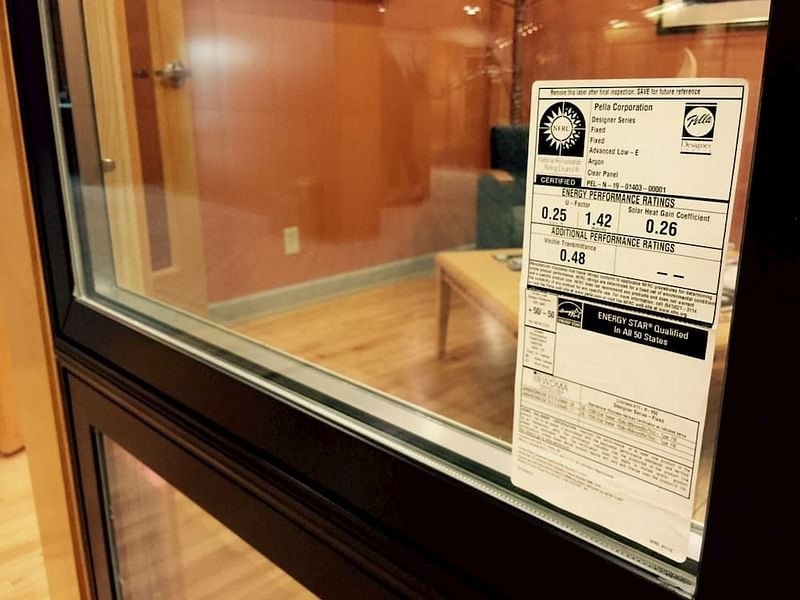
What is the NFRC label?
In addition to simply looking for the ENERGY STAR logo, studying the measurements on your window label can also help you better understand the energy efficiency qualities of your window. ENERGY STAR certified windows or doors have been tested by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) and display an NFRC label on them as verification. The NFRC is an independent, nonprofit organization that rates and certifies windows and doors according to strict requirements. The NFRC doesn’t explicitly recommend which windows to buy, but they provide four different measurements so consumers can easily compare different brands and types of windows. The NFRC’s ratings measure four primary qualities.
4 Qualities of an NFRC Label
1. U-Factor
U-factor is a term used in the construction trade to illustrate the sum of heat passed through the structure of a building, including through windows and doors. Essentially, the U-factor tells you how well windows and doors insulate. U-factor ratings typically fall within as range from .15 to 1.25. The lower the U-factor the better insulation a product will provide.
2. Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
The solar heat gain coefficient, or SHGC, measures how much heat passes through a window, or how effective the window is at keeping out radiant heat from the sun. SHGC is indicated on an NFRC label by a number between 0 and 1. The lower the SHGC rating, the less the window or door transmits solar heat. Typically, the SHGC rating varies between .15 and .80. A product with a high SHGC may permit extra heat from the sun to enter your home during the wintertime, but that additional warmth from the sun can can also generate higher energy bills in the summer when you’re trying to cool your home. The climate in which you live and the direction your home faces are important factors to consider when evaluating the SHGC rating.
3. Visible Transmittance
While SHGC measures the heat that transfers through a window, visible transmittance, or VT, measures how much actual light that is passed through a window. VT ratings are measured as a number between 0 and 1, with a higher number indicating more light transmission. VT might be an important factor to weigh in different parts of your home. For example, you might want windows with a lower VT for a home theatre to keep it darker and enhance the viewing experience.
4. Air Leakage
Air leakage reflects how much air a window will allow into your home. The typical air leakage rating falls between .1 and .03, with a lower number indicating a tighter seal that permits less air to pass through, meaning fewer drafts for you. It’s worth noting that air leakage is an optional rating that not every manufacturer includes on their NFRC labels, and like all NFRC ratings, this measurement assumes proper window installation.
Other Window & Door Label Terms
Low Emissivity (Low- E)
The term low-E refers to a microscopically thin metallic coating on a window. This coating helps lower both the U-factor and SHGC of a window. Another quality many homeowners appreciate about low-E windows and doors is that they block 70% to 95% of the sun’s ultraviolet rays, helping reduce the fading of furniture and carpet.
Insulating Gas
Many windows and patio doors today typically include an insulating gas (commonly argon) between panes of glass, which aids in overall energy performance. Argon is nontoxic, non-reactive, clear, and odorless.
Armed with a better understanding of a product’s performance ratings, you can begin to determine what windows and doors make sense for your home. Different rating ranges make more sense in different parts of the county. To determine what energy-efficiency levels are right for you, plan a visit to your nearest Pella showroom or schedule a free in-home consultation.
Schedule a free consultation to find windows and doors for your home.
